|
TANAKA develops low-temperature Sintering Technology using Silver Nano Ink, and full-surface Silver Metal Film Forming Technology using Etching Processes
New technologies expected to reduce thickness, increase flexibility, and enhance image quality for touch panels and organic electroluminescence displays
TOKYO, Sep 12, 2018 - (ACN Newswire) - TANAKA Precious Metals (TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo) has developed a new wire forming technology capable of sintering at low temperatures using the Company's low-temperature (70°C) sintered silver nano ink ('a low-temperature sintered silver nanometal printing technique'), and a full-surface silver metal film forming technology using existing etching[1] processes ('a full-surface silver metal film forming technique').
 | | Low-temperature sintered silver nano ink |
 | | Full-surface silver metal film |
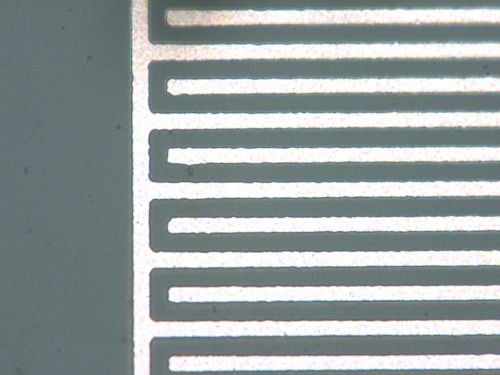 | | 5 micrometers pattern by photolithography |
This technology will contribute to thinner devices, increased flexibility, and higher image quality of smartphone touch panels, organic electroluminescence displays, andother applications.
FEATURES: Low-temperature sintered silver nanometal printing technique
- Previous silver nano ink sintering was only possible at high temperatures of 130-140°C, which made it difficult to print on organic materials such as the comparatively heat-sensitive PET film and other engineering plastic[2] films. However, the newly developed low-temperature sintered silver nanometal printing technique achieves a resistance of 50 micro-ohm centimeters or less, which is equivalent to sintering at high temperatures, even at the low sintering temperature of 70°C. This has dramatically improved the freedom to choose organic materials on which to print.
- Sintering silver nano wire circuitry at the low temperature of 70°C does not damage materials such as organic luminescence elements[3] and contributes to enhanced image quality.
- Patterns formed by low-temperature sintering can consist of several layers to several dozen layers of silver nanoparticles to create multilayer sintered thin film structures, which is expected to provide improved bending strength (flexibility) compared to previous products.
The combination of low-temperature sintered silver nano ink with TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo's SuPR-NaP[4] technique-based metal mesh wiring technology[5] enables fine wires of 4 micrometers or less to be formed on the film.
FEATURES: A full-surface silver metal film forming technique.
- By sintering low-temperature sintered silver nano ink at 140°C, it is possible to form full-surface silver metal films capable of etching and with an equivalent or better level of electrical resistance to that achieved by indium tin oxide (ITO), which is commonly used in current touch panels and other devices.
- Capital investment and other costs can be reduced because existing etching processes can be used.
- Silver metal mesh substrates formed with this technology have an equivalent or better level of electrical resistance to that achieved by transparent electrodes[6] made from indium tin oxide (ITO) etched into a glass substrate. With improved bending strength (flexibility) and improved transparency as well, they are expected to enable enhanced image quality.
As a result of the advantages offered by these products, application in high-end smartphone touch panels, which are expected to shift to bendable displays, and uses and applications in the flexible electronic device market, which is projected to grow, and the organic electroluminescence display market, which is looking for thinner products and enhanced image quality, are expected.
[1] Etching: Also referred to as chemical cautery. Two types, wet etching, and dry etching are used, and both are used to remove the unneeded thin film when forming wiring on a printed circuit board.
[2] Engineering plastics: Mainly used in industrial applications, engineering plastics have specific enhanced functionality, such as strength and heat resistance.
[3] Organic luminescence elements: This refers to organic materials that emit light in response to stimulation by certain types of energy. Also referred to as organic electroluminescence elements or organic light-emitting diodes (OLED).
[4] SuPR-NaP technique: On a substrate (PET film, etc.) coated with liquid-repellent fluororesin, silver nano ink reacts to parts that are modified with deep ultraviolet light. Then, silver nanoparticles undergo chemisorption so that the silver nanoparticles fuse to each other and form wiring.
[5] TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo's metal mesh wiring technology: Metal mesh is a wiring format in a grid pattern that uses silver or copper for sensor wires rather than indium tin oxide (ITO). TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo developed this technology under consignment from April 2014 to September 2017 based on the SuPR-Nap fine wire forming technology resulting from research conducted by Professor Tatsuo Hasegawa, Principal Research Manager at the Flexible Electronics Research Center of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, and others. Development was consigned to TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo under the Joint Industry-Academia Practical Application Development Project (NexTEP).
[6] Transparent electrodes: These electrodes are used in electronic display devices such as LCD displays, organic electroluminescence displays, touch panels,and organic photovoltaic displays. In all cases, the use of etched indium tin oxide (ITO) on glass or other substrates is in wide use.
About TANAKA Precious Metals Group
Since its foundation in 1885, TANAKA Precious Metals Group has built a diversified range of business activities focused on precious metals. TANAKA is a leader in Japan regarding the volumes of precious metals handled. Over the course of many years, TANAKA Precious Metals has not only manufactured and sold precious metal products for industry but also provided precious metals in such forms as jewelry and resources. As precious metals specialists, Group companies within and outside Japan work together with unified cooperation between manufacturing, sales, and technological aspects to offer products and services. Making further progress in globalization, TANAKA welcomed Metalor Technologies International SA as a member of the Group in 2016.
The five core companies of the TANAKA Precious Metals Group are:
-- TANAKA Holdings Co., Ltd.
-- TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo K.K.
-- TANAKA Denshi Kogyo K.K.
-- Electroplating Engineers of Japan, Limited
-- TANAKA Kikinzoku Jewelry K.K.
TANAKA Precious Metals: http://www.tanaka.co.jp/english; Industrial Products http://pro.tanaka.co.jp/en
Press release in PDF: http://www.acnnewswire.com/clientreports/598/180912_EN.pdf
Press inquiries:
TANAKA Holdings/Precious Metals Group.
https://www.tanaka.co.jp/en/protanaka/inquiry/index.php
Source: TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL GROUP Co., Ltd.
Sectors: Metals & Mining, Electronics, Science & Nanotech, Engineering
Copyright ©2025 ACN Newswire. All rights reserved. A division of Asia Corporate News Network. |
Latest Release

Fujitsu launches gen AI software analysis and visualization service to support optimal modernization planning
Feb 04, 2025 11:39 JST
| 
Eisai to Provide Guidance on Reducing the Risk of Cognitive Decline and Nutrition, and Development Guidelines for Home Delivery Meals/Meal Kits to Food-Related Companies
Feb 03, 2025 17:23 JST
| 
MHI Group Presents "Best Innovation 2024" Awards for Products and Activities that Contribute to Solving Social Issues
Feb 03, 2025 14:31 JST
| 
Fujitsu and Tokai National Higher Education and Research System leverage explainable AI to enhance space weather prediction in collaboration with JAXA
Feb 03, 2025 12:05 JST
| 
Enjoy Anime Tokyo Station in the Metaverse! ANIME TOKYO STATION ON ROBLOX Opens at 3:00 p.m. on January 31, 2025!
Feb 01, 2025 08:00 JST
| 
DENSO Announces Third Quarter Financial Results
Jan 31, 2025 18:09 JST
| 
Rally Driver Hiroshi Masuoka Receives the Person of Sports Merit Award in Japan
Jan 31, 2025 15:12 JST
| 
TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL TECHNOLOGIES Launches Visi Fine(R): A Group of Precious Metal Materials for Medical Device Components
Jan 31, 2025 11:00 JST
| 
Mazda Production and Sales Results for December 2024 and for January through December 2024
Jan 30, 2025 16:44 JST
| 
Lexus Announces Global Sales Results for 2024
Jan 30, 2025 15:52 JST
| 
MHI Thermal Systems Receives 2024 Agency for Natural Resources and Energy Commissioner's Award from ECCJ for TEJ35AM Electric-Driven Transport Refrigeration Unit Integrated with Isuzu's ELF EV
Jan 30, 2025 14:13 JST
| 
Mitsubishi Shipbuilding Receives Order for an Offshore Patrol Vessel from the Indonesian Maritime Security Agency
Jan 30, 2025 12:35 JST
| 
Fujitsu and Asepeyo collaborate to modernise the management of occupational benefits and contingencies
Jan 30, 2025 11:56 JST
| 
Suzuki, Daihatsu, and Toyota Decide on the Release Schedule for Mini-Commercial Van Electric Vehicles
Jan 30, 2025 10:56 JST
| 
NEC combines video analysis technology with generative AI to generate advice for improving work quality
Jan 29, 2025 10:08 JST
| 
Japan's Telecommunications Carriers Strengthen Disaster Response by Conducting Joint Training for Shared Refueling Stations
Jan 28, 2025 17:39 JST
| 
FDA Approves LEQEMBI (lecanemab-irmb) IV Maintenance Dosing for the Treatment of Early Alzheimer's Disease
Jan 28, 2025 09:46 JST
| 
Ogier's milestone Monte win crowns TOYOTA GAZOO Racing one-two
Jan 27, 2025 17:24 JST
| 
Anime Tokyo Station: Let's Enjoy together!! History of Anime Series "OSHI NO KO"
Jan 27, 2025 13:00 JST
| 
hootfolio, Inc., a Provider of Causal Analysis Technology, Launches Business Development
Jan 27, 2025 12:01 JST
|
More Latest Release >>
|